Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble antioxidant that’s vital for immune defense, skin health, collagen production, and iron absorption. Unlike many animals, humans can’t synthesize vitamin C, making daily intake through food or supplements essential. In this post, you’ll learn why vitamin C is crucial, symptoms of deficiency, the best food sources, and how to maximize absorption.
What Does Vitamin C Do in the Body?
Vitamin C acts as a powerful antioxidant and cofactor in numerous enzymatic reactions throughout the body.
✔ Key Functions of Vitamin C:
- Boosts immune system response
- Promotes collagen production for skin, tendons, and ligaments
- Enhances iron absorption from plant-based foods
- Protects cells from oxidative stress
- Aids in wound healing and tissue repair
💡 Did You Know? Vitamin C is highly concentrated in immune cells and rapidly depleted during infections.
Top Health Benefits of Vitamin C

✔ 1. Strengthens Immunity
Vitamin C boosts white blood cell function and may reduce the duration and severity of common colds.
✔ 2. Promotes Youthful, Healthy Skin
Essential for collagen production, vitamin C helps maintain skin elasticity and reduces the appearance of wrinkles.
✔ 3. Supports Wound Healing and Tissue Repair
Vitamin C promotes faster healing of cuts, burns, and surgical wounds.
✔ 4. Enhances Iron Absorption
Helps convert plant-based (non-heme) iron into a form your body can better absorb.
✔ 5. Protects Against Oxidative Stress
Neutralizes harmful free radicals, potentially reducing risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.
Signs of Vitamin C Deficiency
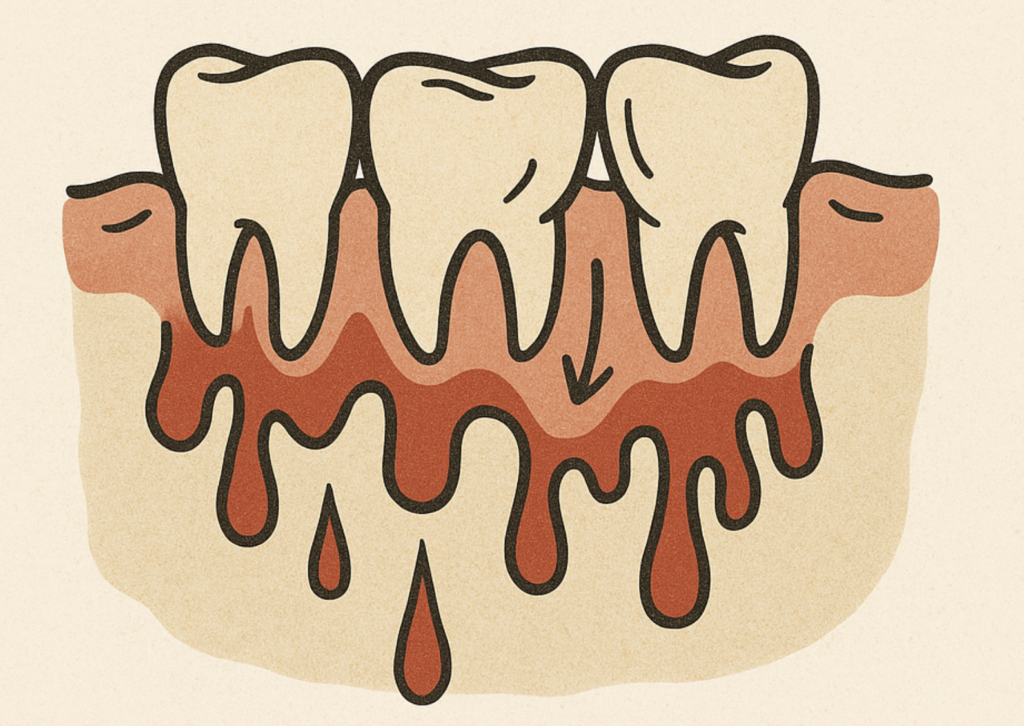
⚠️ Common Symptoms:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Dry, rough, or splitting skin
- Slow wound healing
- Frequent infections
- Bleeding gums and loose teeth
- Easy bruising
💡 Severe Deficiency: Can lead to scurvy, characterized by anemia, gum disease, and bleeding under the skin.
Best Food Sources of Vitamin C

🍊 Fruits:
- Oranges, strawberries, kiwi, guava, papaya
- Grapefruit, pineapple, and cantaloupe
🥦 Vegetables:
- Bell peppers (especially red)
- Broccoli and Brussels sprouts
- Kale, spinach, and cabbage
- Tomatoes and potatoes
💡 Tip: Vitamin C is sensitive to heat and light. Eat raw or lightly cooked fruits and vegetables to preserve the nutrient.
Recommended Daily Intake (RDI)
- Adult men: 90 mg/day
- Adult women: 75 mg/day
- Pregnant women: 85 mg/day
- Breastfeeding women: 120 mg/day
- Smokers: Add 35 mg/day extra (smoking depletes vitamin C)
Vitamin C Supplement Considerations
💊 Forms Available:
- Ascorbic acid (basic form)
- Ester-C (calcium ascorbate, gentler on the stomach)
- Liposomal vitamin C (enhanced absorption)
⚠️ Too Much Vitamin C?
- High doses (>2,000 mg/day) may cause digestive upset (diarrhea, cramps).
💡 Best Practice: Divide doses throughout the day if supplementing above 500 mg for better absorption.
Pros and Cons of Vitamin C
✔ Pros:
- Boosts immune health, skin glow, and wound healing
- Enhances iron absorption
- Potent antioxidant protection
⚠️ Cons:
- Easily destroyed by heat and cooking
- Very high doses can cause GI upset
- Water-soluble—excess amounts are excreted, not stored
Vitamin C is a nutritional powerhouse that helps defend your immune system, rejuvenate your skin, and support wound healing. Aim to include a rainbow of fruits and vegetables in your daily diet to naturally boost your vitamin C intake, and consider supplements during periods of high stress or illness for extra support.
Read more on biotin for hair, skin, and energy support
Learn more about vitamin C from the National Institutes of Health
