You’ve probably heard of vitamin D, magnesium, or iron—but what about choline? This essential nutrient is often forgotten, yet it plays a critical role in brain function, hormone regulation, liver detox, and even fetal development. In fact, many people—especially women—don’t get enough choline through diet alone. In this post, you’ll learn why choline is vital, the symptoms of deficiency, and how to naturally boost your intake for better health and vitality.
What Is Choline and Why Is It Important?
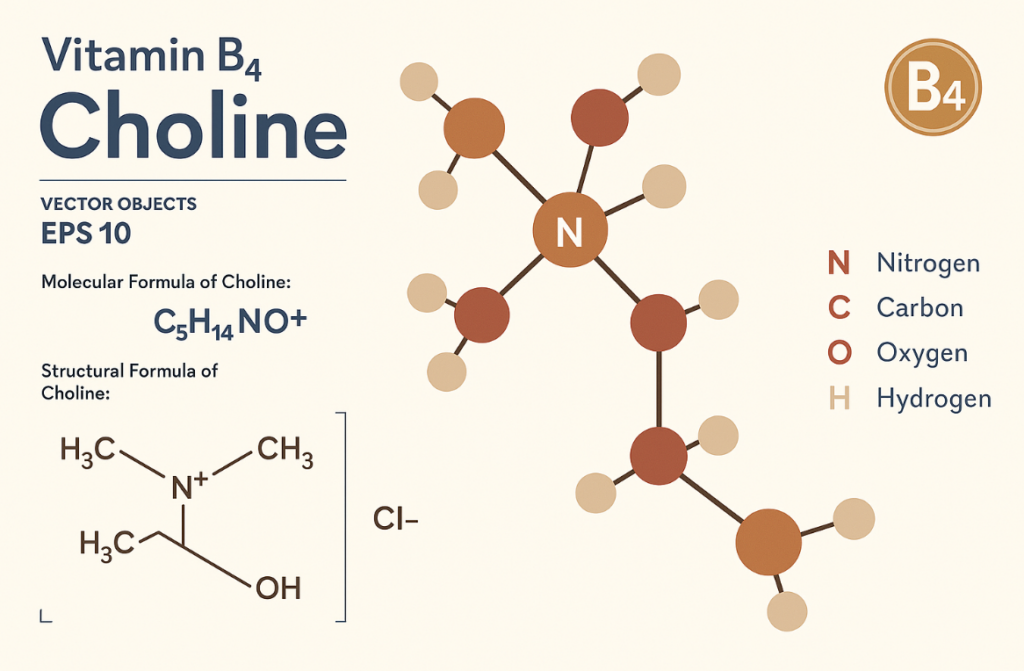
Choline is a water-soluble nutrient that behaves like both a vitamin and a coenzyme. Your body can produce small amounts, but you need to get most of it from food.
✔ Core Roles of Choline:
- Builds acetylcholine, a key neurotransmitter for memory, focus, and learning
- Assists in methylation (used in DNA expression, detox, and estrogen metabolism)
- Helps form cell membranes (especially in the brain and liver)
- Prevents fatty liver by exporting fat from the liver to the bloodstream
- Supports fetal brain development and reduces neural tube defect risk
💡 Did You Know? Up to 90% of Americans don’t meet the recommended choline intake, especially women of reproductive age.
Choline and Brain Function
Choline is a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for:
- Learning and memory formation
- Neuroplasticity (brain adaptability)
- Muscle control
- Sleep regulation
Low choline = brain fog, poor memory, trouble concentrating, and even mood changes.
Choline and Hormone Health
Choline is involved in methylation, a biochemical process that influences:
- Estrogen metabolism (prevents buildup of harmful estrogen metabolites)
- Cortisol regulation (stress recovery)
- Gene expression related to inflammation, mood, and detox pathways
This makes choline crucial for people with:
- Estrogen dominance or heavy PMS
- PCOS or infertility
- Thyroid dysfunction
Choline and Liver Health
Without enough choline, fat accumulates in the liver—leading to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Choline helps package and export triglycerides from the liver to the bloodstream, where they can be used for energy.
Symptoms of liver-related choline deficiency:
- Bloating or right-side abdominal discomfort
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Brain fog or fatigue after eating
Choline in Pregnancy and Child Development
Choline is crucial during pregnancy, especially for fetal brain and spinal cord development. It works alongside folate (B9) to prevent neural tube defects and supports long-term cognitive outcomes in infants.
💡 Fun Fact: Choline demand increases by up to 50% during pregnancy, yet most prenatal vitamins do not contain enough (if any) choline!
Signs You May Be Low in Choline
⚠️ Symptoms of deficiency:
- Brain fog, poor concentration
- Anxiety or mood swings
- Fatigue that doesn’t resolve with sleep
- Fatty liver or liver enzyme elevation
- PMS, hormone imbalances, or PCOS symptoms
- Digestive issues or poor methylation (histamine intolerance, B12 deficiency)
Best Food Sources of Choline
🥚 Animal-Based Sources (highest):
- Egg yolks (1 yolk = ~147 mg choline)
- Liver (beef, chicken)
- Salmon, sardines, cod
- Chicken and turkey
- Grass-fed beef
🌿 Plant-Based Sources (moderate):
- Brussels sprouts, broccoli, cauliflower
- Quinoa and wheat germ
- Soybeans and tofu
- Shiitake mushrooms
💡 Tip: 2–3 egg yolks a day can cover 50–75% of your daily choline needs!
How Much Choline Do You Need?
- Adult women: 425 mg/day
- Pregnant women: 450–550 mg/day
- Adult men: 550 mg/day
Should You Supplement Choline?
💊 Forms Available:
- Alpha-GPC or CDP-Choline: Best for brain function
- Choline bitartrate or lecithin: General use
- Phosphatidylcholine: Found in sunflower or soy lecithin (often in supplements)
⚠️ Note: High-dose choline may cause a fishy body odor in sensitive individuals due to gene variants (FMO3).
Choline may not be trendy, but it’s one of the most powerful nutrients for brain sharpness, hormonal resilience, and liver protection. Whether through egg yolks, liver, or targeted supplementation, getting enough choline daily can help prevent burnout, balance mood, support detox, and promote long-term cognitive health.
Read more on building an anti-inflammatory plate for hormone health
Learn more about choline from the NIH Office of Dietary Supplements