Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats your body can’t make on its own, yet they play a powerful role in everything from brain function and heart health to inflammation and mood. If you’re not eating fatty fish regularly—or following a plant-based diet—you may be missing out. In this post, you’ll learn what omega-3s do, how to get them naturally, signs of deficiency, and how to choose the best supplements for your goals.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3s are a group of polyunsaturated fats that support cell membrane structure and anti-inflammatory activity. There are three main types:
✔ Types of Omega-3s:
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid): Found in plant foods like flaxseeds and walnuts
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid): Found in marine sources like fish and algae
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid): Also in fish; crucial for brain and eye health
💡 Did You Know? ALA must be converted to EPA and DHA in the body—but this process is inefficient (under 10%).
Top Health Benefits of Omega-3s
✔ 1. Protects Heart Health
Omega-3s lower triglycerides, reduce blood pressure, prevent clotting, and help regulate heart rhythm.
✔ 2. Supports Brain Function and Mental Health
DHA is a major structural fat in the brain. Omega-3s are linked to improved cognition, mood, and may reduce depression or ADHD symptoms.
✔ 3. Reduces Inflammation
EPA helps balance your body’s inflammatory response, easing joint pain, autoimmune symptoms, and chronic inflammation.
✔ 4. Improves Eye Health
DHA makes up 60% of the retina. Adequate omega-3s may protect against dry eyes and macular degeneration.
✔ 5. Supports Prenatal and Infant Development
Omega-3s (especially DHA) are vital for brain, nerve, and eye development in the fetus and during early childhood.
✔ 6. May Improve Skin Health
Omega-3s help hydrate skin, reduce acne inflammation, and protect against sun damage.
Signs of Omega-3 Deficiency
⚠️ Common Symptoms:
- Dry skin or hair
- Brain fog or poor memory
- Mood swings or depression
- Joint stiffness or inflammation
- Fatigue and trouble concentrating
💡 At-Risk Groups:
- People who rarely eat fish
- Vegans and vegetarians
- Individuals with inflammatory or autoimmune conditions
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
Best Dietary Sources of Omega-3s
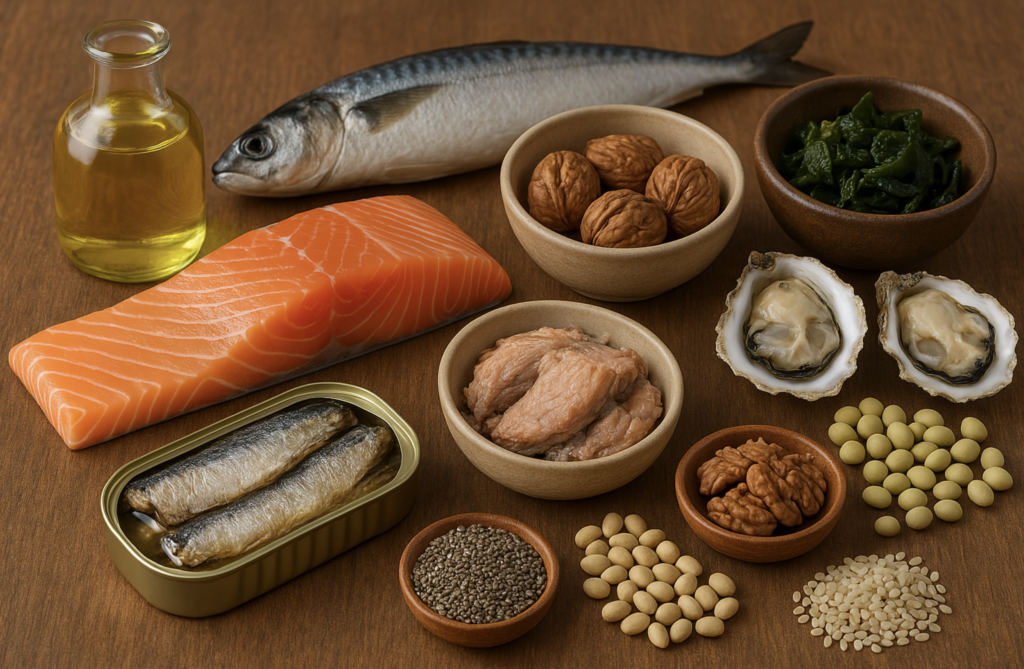

🐟 Marine-Based (rich in EPA and DHA):
- Salmon, mackerel, sardines, anchovies, herring
- Cod liver oil
- Oysters and trout
🌱 Plant-Based (rich in ALA):
- Chia seeds and flaxseeds
- Walnuts
- Hemp seeds and soybeans
- Seaweed and algae (only plant source of DHA)
💡 Tip: Pair omega-3 foods with healthy fats like avocado or olive oil for better absorption.
Recommended Daily Intake
There’s no formal RDA, but general guidelines suggest:
- EPA + DHA (combined): 250–500 mg/day for healthy adults
- ALA: 1.1 g/day for women, 1.6 g/day for men
- Higher needs for heart disease, pregnancy, or inflammation
Omega-3 Supplement Considerations
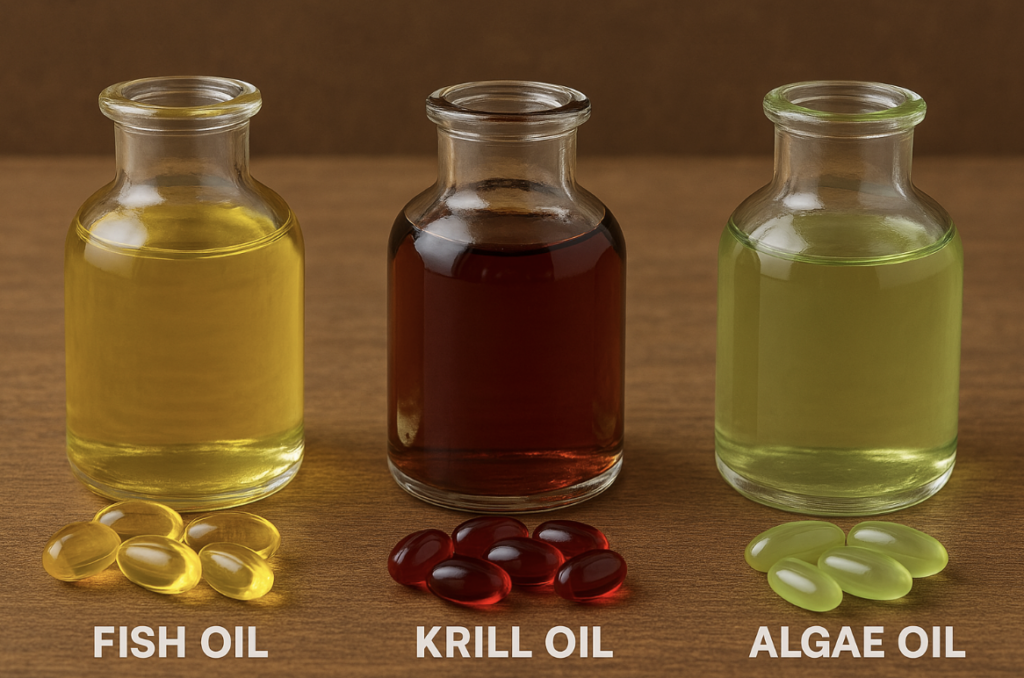

💊 Popular Options:
- Fish oil (EPA/DHA): Most common and well-studied
- Krill oil: Better absorbed, contains antioxidants
- Algae oil: Best plant-based source of DHA for vegans
⚠️ What to Watch Out For:
- Check for purity and heavy metal testing (especially in fish oil)
- Avoid oxidized oils (look for dark glass bottles or capsules with vitamin E)
💡 Tip: Take omega-3 supplements with meals for better absorption and to prevent fishy burps.
Pros and Cons of Omega-3s
✔ Pros:
- Supports heart, brain, joints, skin, and eyes
- Naturally anti-inflammatory
- Easy to supplement and widely available
⚠️ Cons:
- Low conversion rate from ALA to EPA/DHA
- Some supplements can cause digestive upset or fishy aftertaste
- Risk of contamination in poorly sourced oils
Omega-3s are essential to nearly every system in your body—yet many people don’t get enough. Whether through fish, flaxseeds, or a clean supplement, prioritizing these healthy fats is a simple and effective way to boost heart health, brain clarity, and long-term wellness.
Read more on how calcium suppers bone health naturally
Learn more about omega-3s from Harvard School of Public Health
